As a health-conscious community, we recognize the escalating concern surrounding obesity—a condition plaguing millions with its multifaceted health risks. It is now more crucial than ever to promote obesity prevention and heighten obesity awareness. In undertaking this important conversation, we explore the pervasive impact of obesity, emphasizing the urgency for informed action and support.
Our navigational guide through the complex terrain of obesity aims to equip you with the knowledge to prevent its onset and manage it effectively, should it affect you or your loved ones. Join us as we delve into the depths of obesity, uncovering the essential information needed to combat this health adversary.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the gravity of obesity and its widespread impact on health.
- Identifying critical strategies for obesity prevention.
- Enhancing obesity awareness to incite proactive health management.
- Highlighting actionable insights to mitigate obesity-related health risks.
- Empowering individuals with knowledge for a healthier, balanced lifestyle.
What is obesity?

When we talk about obesity, we refer to a health condition characterized by excessive body fat that increases the risk of chronic diseases and health problems. As medical professionals and concerned citizens alike address this pressing issue, it remains imperative to cover not just the obesity definition but also draw a distinction between being overweight and being obese. Understanding the causes of obesity is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
While the term ‘overweight’ depicts an excess in body weight in relation to height, obesity is specifically associated with the amount of excess body fat. This distinction is crucial as it impacts both the approach to and the necessity for medical intervention. To elucidate further, let’s present a comparison through an informative table:
| Criterion | Overweight | Obesity |
|---|---|---|
| Body Mass Index (BMI) Range | 25-29.9 | 30 and above |
| Health Risk Level | Moderate | High |
| Physical Appearance | May not have visible excess body fat. | Visible excess body fat |
| Common Causes | Physical inactivity and an unhealthy diet | Genetics, metabolic factors, and lifestyle habits |
| Prevention Strategies | Caloric intake monitoring, increased physical activity | Medical evaluation, targeted weight loss programs, and lifestyle modification |
Recognizing the causes of obesity extends beyond acknowledging the caloric imbalance between what is consumed and what is expended. Our aim is to present a nuanced picture that takes into account the multitude of factors that can lead to obesity, such as genetic predispositions, metabolism differences, and environmental conditions, which could all play significant roles.
- Genetic Factors: Individuals can inherit a tendency toward obesity from their parents.
- Socioeconomic Status: Limited access to healthy foods and recreational spaces can lead to higher obesity rates in certain communities.
- Lifestyle Choices: Sedentary behavior and high-calorie diets are common contributors to excess body weight.
- Psychological Influences: Emotional factors, such as stress and depression, have been identified to contribute to overeating.
As we deepen our understanding, it is clear that effectively addressing obesity involves a comprehensive approach. By recognizing the diverse elements at play, we are better poised to advocate for and customize strategies for prevention and treatment tailored to the unique needs of each individual facing this condition.
Obesity in America: A Growing Concern
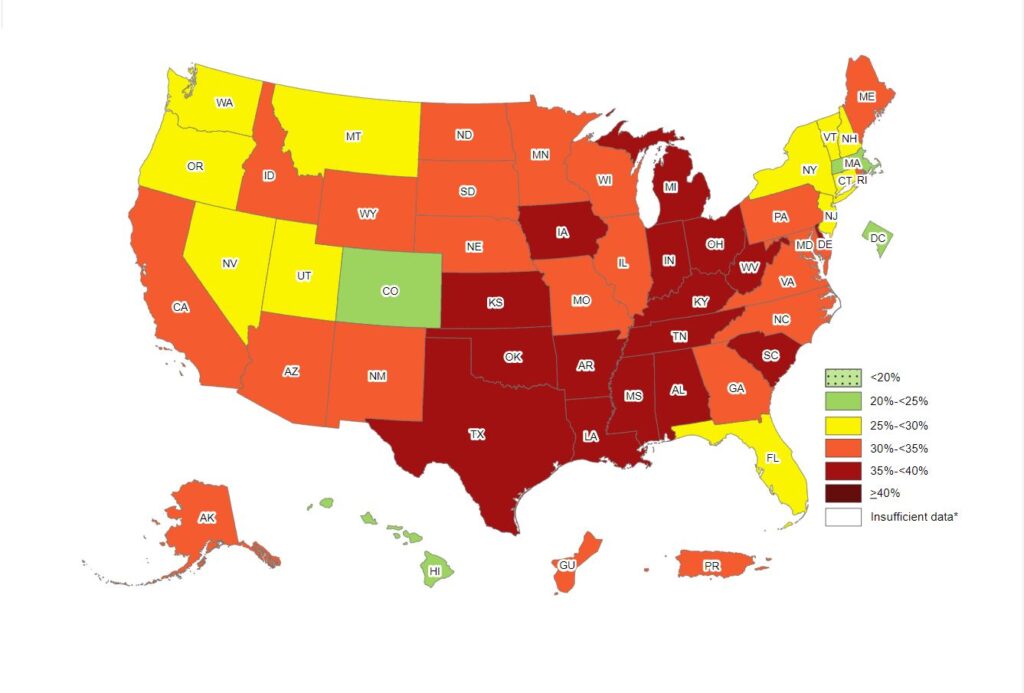
Obesity in America is not just a health issue but a burgeoning epidemic that affects millions and poses a serious economic strain on our healthcare system. As we untangle the web of obesity statistics, we are confronted with a complex and distressing picture of the nation’s health. Our mission is to shine a light on the gravity of the situation, providing our readers with a deep-dive analysis of current trends and demographic impacts.
Recent statistics from credible health authorities reveal that obesity rates have reached unprecedented levels. The numbers reflect a harsh reality: a significant portion of our population is grappling with the weight of this condition, quite literally. This data is not just a gauge of present circumstances; it represents a trajectory that, if not altered, predicts a future burdened with chronic disease, reduced life expectancy, and soaring healthcare costs.
Let’s consider the data in its stark form, represented across different demographics:
| Age Group | Obesity Prevalence | Trend Over the Past Decade |
|---|---|---|
| Children (2–19 years) | 19.3% | Rising |
| Adults (20–39 years) | 40.0% | Steadily Increasing |
| Middle-aged (40–59 years) | 44.8% | Sharply Increasing |
| Seniors (60 years of age and older) | 42.8% | Stabilizing |
Beyond age demographics, obesity in America also disproportionately affects certain ethnic and socioeconomic groups. This disparity suggests that more than individual lifestyle choices, systemic factors contribute to the prevalence of obesity. Factors such as access to healthy food, opportunities for regular exercise, and even educational outreach about the importance of maintaining a healthy weight play a significant role in the national trend.
In our exploration, it becomes evident that the fight against obesity is not waged on a single front. It’s a multi-faceted challenge that requires concerted effort from policymakers, healthcare providers, communities, and individuals alike. As we unfold the layers of this complex issue, our goal is to empower our readers with the knowledge to understand the scope of this concern and to take informed steps towards a healthier future for America.
Unpacking the Causes of Obesity

As we delve into the complexities of obesity, it’s essential to understand the multifaceted nature of its causes. Going beyond common assumptions, our focus shifts to the interplay between genetic predispositions, the intricacies of lifestyle choices, and the often-overlooked impact of the socio-economic environment. These elements collectively sketch the landscape of obesity causes and pave avenues for obesity prevention.
Genetic Factors in Obesity
Genetics play a crucial role in an individual’s susceptibility to obesity. Certain genes can affect metabolism, appetite, and the body’s ability to convert food into energy. While not determinants, they certainly influence the ease with which someone may gain weight. Identifying these genetic factors is pivotal for understanding risk and tailoring prevention strategies.
Lifestyle Choices Leading to Weight Gain
Lifestyle choices stand at the forefront of obesity causes. Diet, characterized by high calorie intake, and sedentary behaviors collectively contribute to weight gain. Active choices in favor of balanced nutrition and regular physical activity can substantially mitigate these risks and act as a cornerstone for obesity prevention and management.
The Impact of the Environment on Obesity
The environment in which one lives can significantly influence their likelihood of becoming obese. Access to healthy food options, safe spaces for exercise, and even societal norms play a role. Addressing environmental barriers and fostering support systems are critical in the collective fight against the obesity epidemic.
Decoding Obesity Statistics
As we delve into obesity statistics, it’s essential to frame the data within the context of obesity awareness. In recent years, the illumination of obesity trends has become a pivotal part of health discourse in America. We analyze the numbers not merely to grasp their magnitude but to understand their implications for society and health policy. By interpreting these figures, we aim to provide a comprehensive view that goes beyond the surface to reveal how obesity unevenly affects various demographics and regions across the country.
Obesity statistics paint a stark picture of an escalating public health challenge. Behind each percentage and data point lies a unique narrative of dietary habits, socio-economic status, cultural influences, and educational outreach efficacy. Our examination will unearth these narratives, providing clarity on the persistent increase in obesity rates and spotlighting areas where obesity awareness efforts may be redoubled.
| Age Group | Obesity Rate | Change Over Time |
|---|---|---|
| Adults 20-39 | 40.3% | +4% increase in the past decade |
| Adults 40-59 | 44.8% | +3% increase in the past decade |
| Adults 60+ | 42.8% | +2% increase in the past decade |
We can’t ignore the geographical variations that emerge from obesity statistics. Disparities prevalent across different states and communities suggest that where you live can significantly influence your risk of becoming obese. Southern states, for example, have historically reported higher rates of obesity compared to other regions, implicating a mix of dietary customs, quality of health education, access to nutritious food, and the availability of safe spaces for physical activity.
To render these statistics actionable, it is our duty to foster obesity awareness. Recognizing the factors that contribute to these trends is the first step. We work to dispel myths, provide clear guidance, and advocate for health policy changes geared towards making the healthy choice the easy choice. Through understanding and acting upon these obesity statistics, we envisage a path forward towards healthier communities across the United States.
Comprehensive Obesity Definition
Understanding the definition of obesity is crucial in differentiating it from being merely overweight. Obesity is not just about excess weight; it is a medical condition characterized by an accumulation of body fat that may impair health. Here, we dissect the terminology and tools used to assess and classify weight status, such as the Body Mass Index (BMI), an invaluable index for identifying obesity health risks.
Differentiating Between Overweight and Obesity
While the terms ‘overweight’ and ‘obesity’ are often used interchangeably, there’s a significant distinction between the two based on the Body Mass Index. Being overweight refers to having a BMI that is higher than what is normally considered healthy for a given height but lower than the obesity range. Obesity is defined as having a BMI that is considerably above the healthy range. This distinction is critical as it pertains to the severity of associated health risks.
Body Mass Index (BMI): A Tool for Assessing Weight
BMI is a widely recognized formula that uses height and weight to calculate a numerical value. While not a direct measure of body fat, it correlates with more complex health measures and provides a simplified metric to categorize weight status, thereby aiding in the identification of potential obesity health risks.
| BMI Range (kg/m2) | Weight Status | Associated health risks |
|---|---|---|
| Under 18.5 | Underweight | Malnutrition, vitamin deficiencies, and anemia |
| 18.5–24.9 | Normal or healthy weight | Lower risk of chronic diseases |
| 25.0–29.9 | Overweight | Increased risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension |
| 30.0 and above | Obese | Higher risk of type 2 diabetes, cancer, and stroke |
By employing the BMI as a baseline assessment, we can start to understand and address the obesity health risks presented by higher weight categories. It is a step towards a more profound comprehension of obesity as a multi-faceted health challenge.
Identifying Obesity Health Risks
As we delve into the implications of obesity, understanding the health risks associated with the condition is paramount. Far beyond the common understanding that obesity leads to hypertension and diabetes, there are several less conspicuous health risks that need our undivided attention. These risks highlight the pressing need for effective weight loss strategies and proactive obesity treatment.
| Health Risk | Description | Relevance to Obesity |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | Conditions that involve blocked or narrowed blood vessels. | Obesity increases strain on the heart, potentially leading to heart attacks or strokes. |
| Type 2 diabetes | Chronic condition affecting the way the body processes blood sugar. | Excess body fat contributes to insulin resistance, elevating diabetes risk. |
| Certain Cancers | Obesity is linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer. | Fat tissue produces excess hormones and inflammation, both of which can contribute to cancer risk. |
| Osteoarthritis | A degenerative joint disease causing pain and stiffness. | Extra weight places additional stress on joints, exacerbating wear and tear. |
| Sleep Apnea | A disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep. | Fat deposits around the upper airway can obstruct breathing, which is common in obese individuals. |
| Fatty liver disease | Excess fat buildup in the liver leads to inflammation and liver damage. | Associated with metabolic syndrome and increased in prevalence with obesity. |
The aforementioned health risks are only the tip of the iceberg. Our aim in highlighting these conditions is not to alarm but to inform and educate. Each of these health complications can significantly reduce the quality of life and increase mortality risk, making effective weight loss and holistic obesity treatment not just advisable but essential.
Remember, tackling obesity is not solely about improving aesthetic appeal but, more importantly, about enhancing overall health and longevity.
Obesity Prevention: Strategies for a Healthier Life

As we continue our deep dive into the subject of obesity, our emphasis shifts toward empowering strategies aimed at halting this widespread issue. Obesity prevention is a multifaceted approach that involves a combination of a well-rounded, balanced diet, consistent physical activity, and meaningful behavioral changes. These elements are pillars of a lifestyle that promotes weight loss and the maintenance of a healthy weight. Let’s delve into these crucial components one by one.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is fundamental for obesity prevention. It provides the body with essential nutrients while managing calorie intake. The goal is not only to lose weight but also to nourish the body. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can significantly impact one’s health journey.
Physical Activity: A Key Component in Weight Management
Engaging in regular physical activity stands out as a critical aspect of weight loss and obesity prevention. Exercise aids in burning calories, increasing muscle mass, and improving overall health. Whether it’s a daily walk, a jog, or strength training, incorporating movement into one’s routine is a step towards a vigorous life.
Behavioral Changes for Long-Term Success
Long-term success in preventing obesity lies in the adoption of behavioral changes. This means altering habits and mindsets to make healthier choices more naturally. Strategies such as setting realistic goals, keeping a food diary, and seeking social support can make a significant difference in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Portion Control | Mindful eating with attention to serving sizes | Reduces calorie intake without feeling deprived |
| Meal Planning | Preparing meals ahead to avoid last-minute unhealthy choices | It ensures a balanced intake of nutrients and saves time and money. |
| Regular Exercise | Including both aerobic and strength training exercises | Boosts metabolism, burns calories, and improves mood. |
| Mindfulness | Being present during meals to enjoy food and recognize cues of fullness | Promotes a healthier relationship with food and prevents overeating. |
Our collective journey towards obesity prevention is not a quick fix; it’s a lifestyle transformation. By making conscious decisions about our diet, committing to regular physical activity, and remodeling our behavior for the better, we set the stage for a healthier, more vibrant life. These steps, grounded in evidence-based practice, can help us combat the obesity epidemic and enhance our overall well-being.
Diet and Obesity: Understanding the Relationship

As we explore the intricacies connecting diet to obesity, it becomes evident that what we eat plays a pivotal role in either contributing to or alleviating this global health concern. At the core of enabling weight loss and addressing the causes of obesity is the emphasis on a balanced diet. A harmonious blend of macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals is essential for fueling our bodies and maintaining a healthy weight. To illustrate this point, let’s delve into how various dietary components impact the risk of obesity.
- Caloric surplus: Consuming more calories than expended leads to weight gain.
- Quality of Calories: Calories from nutrient-dense foods versus empty calories have different effects on satiety and metabolic health.
- Macronutrient Composition: A diet high in processed carbohydrates and unhealthy fats may increase the risk of obesity.
- Fiber Intake: Fiber promotes fullness, helping to control appetite and prevent overeating.
- Portion Sizes: Larger portion sizes contribute to increased caloric intake and weight gain.
Reframing our relationship with food involves understanding these dietary components and making informed choices. A balanced diet rich in whole foods, like vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains, can create a foundation for not only preventing obesity but also improving overall health. Conversely, a diet high in refined sugars, saturated fats, and excess sodium can escalate the risk of developing obesity and related health issues.
| Food Category | Recommended Intakes for Weight Management | Common foods to limit or avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and vegetables | 5 servings per day (minimum) | Pre-packaged fruit snacks with added sugars |
| Lean Proteins | 2 servings/day | Fried meats, high-fat cuts |
| Whole Grains | 3 servings/day | Refined bread, sugary cereals |
| Healthy Fats | Moderation | Trans fats, deep-fried foods |
| Dairy or Alternatives | 2 servings/day | High-fat dairy, full-fat cheeses |
Acknowledging the direct linkage between diet and obesity propels us to advocate for dietary education and practical, accessible nutrition resources. By making informed decisions about the food we consume, we not only counter the obesity epidemic but also enhance our overall health and longevity. Shifting towards a balanced diet is an investment in a healthier, more vibrant future for all of us.
Obesity Treatment: An Overview
When we confront the issue of obesity, a multifaceted approach is essential for effective treatment. Diverse strategies are tailored to meet individual needs, fostering weight loss and promoting better health outcomes. Within our discussion, we’ll explore the spectrum of obesity treatment options, from nurturing guidance in nutritional counseling to more direct medical interventions and surgical procedures for those facing severe obesity.
Nutritional counseling and support
Nutritional counseling stands as a cornerstone of obesity treatment, offering personalized dietary plans and professional support. It equips individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary for sustainable weight loss. Tailoring strategies to one’s lifestyle, counselors provide guidance on balanced meal planning, portion control, and understanding the nutritional value of foods.
Medical Interventions for Severe Cases
In cases where obesity poses immediate health risks, medical interventions may be warranted. These can range from prescription weight-loss medications that suppress appetite or reduce fat absorption to hormone therapy treatments that can help rebalance the factors contributing to weight gain.
Surgical Options and Considerations
Surgical options, such as bariatric surgery, are available for patients with severe obesity when other treatments haven’t yielded the desired results. These procedures can significantly reduce the size of the stomach or limit calorie absorption, leading to substantial weight loss. Despite its effectiveness, surgery is a considerable step that requires a thorough evaluation of risks and benefits and a commitment to lifestyle change post-operation.
| Treatment | Description | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Counseling | Professional dietary guidance | Customized eating plans and education on nutritious food choices | Requires consistent follow-through and lifestyle changes. |
| Medical Interventions | Weight loss medications and hormone therapies | Can kickstart weight loss, possibly improving other health markers. | Potential side effects are not suitable for all individuals. |
| Bariatric Surgery | Surgical procedures to reduce stomach size or calorie absorption | Significant weight loss and improvements in obesity-related conditions | It is invasive, carries standard surgical risks, and requires lifestyle adjustments. |
Raising Obesity Awareness: Why It Matters
As we delve deeper into the discussion on obesity in America, it’s evident that obesity awareness plays a pivotal role. Not only does it shape public perception, but it also drives the national agenda toward obesity prevention. We, as a society, must recognize that knowing more about this health issue is the cornerstone of empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being. Awareness is the first step in the battle against obesity.
Consider the statistics—over the past few decades, obesity rates have soared. It’s a clear signal that obesity in America is not just a personal health issue but a burgeoning public health crisis. This upsurge calls for immediate attention and concerted action. By raising awareness, we lay the groundwork for education programs that can dramatically alter the course of this epidemic.
- Spreading knowledge about healthy lifestyle choices
- Highlighting the risks associated with obesity and its associated health conditions
- Championing the successes of those who’ve taken steps to prevent or overcome obesity
- Informing public policy to support healthier food and exercise options
Through awareness campaigns and educational outreach, we not only shed light on the causes and risks but also highlight success stories that can inspire others. We communicate that obesity is preventable and, often, treatable.
Moreover, awareness fosters community support, which is essential for individuals trying to make positive changes. It builds an environment where healthier choices become easier to make and maintain. To that end, obesity prevention measures gain momentum from visibility and public discourse, turning individual efforts into collective action.
Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is not enough; we must do it. – Goethe
We have seen the powerful impact of awareness in other public health initiatives. When we come together to raise awareness about obesity, we are not just sharing information—we are catalyzing change. It’s about creating a healthier future for all and proving that education is as vital as any medicine in our healthcare arsenal.
Living with Obesity: Personal Stories and Successes
Throughout our journey to understand obesity, one of the most compelling aspects has been the personal tales of those who live with it. These narratives do more than just recount struggles; they often shine a light on the incredible successes of individuals who have found ways to manage their weight and improve their health. Let’s explore some of the transformative stories that show the human side of obesity, the challenges faced, and the triumphs that inspire us all.
“Every step I take towards health is a victory, no matter how small it may seem at the time. My journey isn’t just about weight loss; it’s about gaining life.” — Real testimony reflecting the sentiment within the community.
We have seen progress in the fight against obesity, especially when individuals harness nutrition, exercise, and medical support to their advantage. Below, we present a table that highlights several anonymized success stories that have emerged from our readership. The data offers a snapshot of the diversity and scope of what people have achieved in their personal battles with obesity.
| Age Range | Duration of Weight Management Efforts | Weight Loss (lbs) | Health Improvements Noted | Methods Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25-34 | 2 years | 45 | Reduced blood pressure, increased energy | Dietary changes, increased physical activity |
| 35-44 | 6 months | 30 | Improved sleep, lower cholesterol | Professional nutritional counseling and mindfulness practices |
| 45-54 | 1 year | 55 | Better mobility and Type 2 diabetes remission | Weight loss surgery, support groups |
| 55-64 | 18 months | 40 | Joint pain relief, improved heart health | Medical interventions, personal training |
In these stories, we find a common thread of perseverance and resilience, which underscores the belief that personal commitment, when combined with effective strategies, can lead to substantial improvements in living with obesity. Our readers have shared these experiences in the hope of encouraging others, demonstrating that success in managing obesity is achievable and varied.
- Understanding individual needs and challenges
- Adapting to a balanced and nutritious diet
- Incorporating regular exercise into your daily life
- Seeking emotional and professional support when necessary
It’s these practical steps, paired with the determination to make a change, that turn personal stories into successes against obesity. As we have observed, the journey is unique to each person, but the destination of a healthier life is a universal aspiration. These narratives are not just accounts of weight loss; they are affirmations of life reclaimed, health restored, and hope renewed.
Conclusion
In our extensive journey through the complexities of obesity, we’ve unearthed its multifaceted nature and the critical importance of understanding it from various angles. As we stand at the crossroads of knowledge and action, it’s vital that we translate our awareness into tangible steps forward in combating this prevalent health issue. Together, as a society, we possess the collective power to shift the tide on obesity, ultimately paving the way for healthier generations to come.
Moving Forward: Taking Action Against Obesity
As we look toward the future, it’s clear that abating the tide of obesity requires a steadfast commitment to both individual and community action. By embracing informed choices and integrating preventive measures, we can each contribute to a downward trend in obesity rates. Our collective efforts can manifest in advocating for policy changes, creating supportive environments, and prioritizing public health initiatives that facilitate access to healthier lifestyle options.
Empowering Individuals to Make Healthier Choices
Empowerment stands as a cornerstone in the fight against obesity. Through education, support, and resources, we enable individuals to take charge of their own health. The implementation of small but significant lifestyle adjustments, such as choosing nutritious foods and increasing physical activity, can have profound impacts over time. By fostering personal accountability and resilience, we fortify the resolve needed to maintain a healthier life amidst the challenges of modern living.
FAQ
What is obesity, and how is it different from being overweight?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation that may impair health. It is different from being overweight, which is weighing more than what is considered normal or healthy for a certain height. Being overweight is a precursor to obesity, and obesity is typically defined by a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or higher.
Why is obesity considered a growing concern in America?
Obesity is a growing concern in America due to its alarming prevalence and upward trend. According to the latest obesity statistics, a significant portion of the population, including adults and children, is classified as obese. This trend is worrisome because obesity is associated with numerous health risks, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers, and it poses a burden on healthcare systems.
What are the primary causes of obesity?
The causes of obesity are multifaceted, involving genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Genetically, some individuals have a predisposition to obesity. Lifestyle choices, such as consuming high-calorie diets and a lack of physical activity, are significant contributors. Environmental factors, including social and economic challenges, access to healthy foods, and cultural norms, also play a role in the rising rates of obesity.
How do obesity statistics help us understand the severity of the issue?
Obesity statistics provide us with data on prevalence, demographic variations, and time trends, which helps us understand the extent and severity of the obesity epidemic. By examining these statistics, we can identify at-risk populations, observe the effectiveness of public health initiatives, and reinforce the need for increased prevention and treatment efforts.
How is the Body Mass Index (BMI) used to assess weight, and what are its limitations?
BMI is a screening tool that calculates weight in relation to height to categorize individuals as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. While BMI is useful for population-level assessments, it has limitations. It does not directly measure body fat and can misclassify muscular individuals as overweight or individuals with low muscle mass as healthy.
What health risks are associated with obesity?
Obesity increases the risk of numerous health issues, including but not limited to heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, hypertension, sleep apnea, and mental health conditions. It can also lead to complications with reproductive health, respiratory problems, and increased surgical risks.
Can obesity be prevented, and if so, how?
Obesity can be prevented by adopting a lifestyle that emphasizes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and behavioral changes to support healthy eating and movement habits. It’s crucial to address these factors early on to reduce the risk of becoming obese and to encourage a more vibrant and healthier life.
How does diet influence obesity?
Diet plays a pivotal role in the development and management of obesity. High-calorie, nutrient-poor foods contribute to weight gain, whereas a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of obesity.
What treatment options are available for obesity?
A multifaceted approach to obesity treatment includes lifestyle interventions like nutritional counseling and increased physical activity, medical treatments such as weight loss medications, and, in severe cases, surgical options like bariatric surgery. A healthcare provider can recommend the most appropriate treatment based on individual health needs and obesity severity.
Why is raising awareness about obesity important?
Raising awareness about obesity is critical for prevention and treatment. Awareness can lead to early detection and intervention, educational programs that promote healthier lifestyles, and public policies that support health and accessible, nutritious food options. Informed communities are better equipped to combat obesity and support those affected by it.
